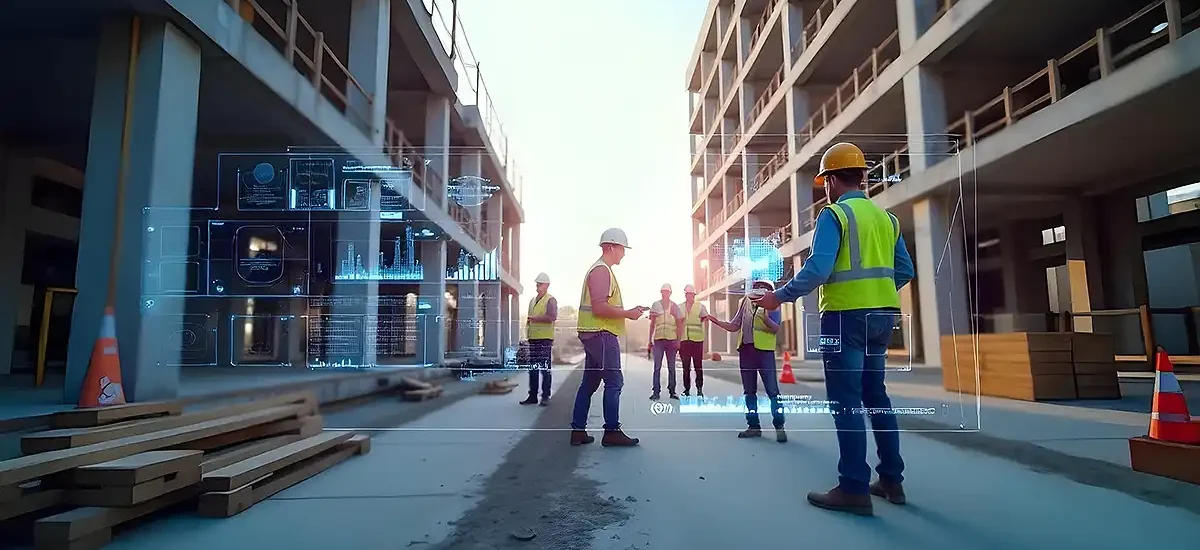
In the construction industry, the role of an MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing)
engineer is essential to creating efficient, sustainable, and safe building environments.
With the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and environmental certification standards
like LEED and BREEAM, MEP engineers play a crucial part in modern construction projects.
They manage everything from HVAC systems to electrical distribution, fire safety, and
water supply, ensuring that each component operates harmoniously. This overview
outlines the core roles and responsibilities of an MEP engineer, providing insight into the
critical functions they serve within a construction company.
1. Conceptual and Detailed Design of MEP Systems
One of the primary responsibilities of an MEP engineer is the conceptual and detailed
design of MEP systems for construction projects. During this phase, MEP engineers work
closely with architects and structural engineers to create a design that integrates
seamlessly with the building layout. This includes HVAC system design for heating,
ventilation, and air conditioning, as well as plumbing services that ensure reliable water
supply and waste removal.
To ensure efficiency, MEP engineers carry out feasibility studies and engineering
technology advice to optimize building performance. They also prepare detailed designs
that account for thermal loads, lighting intensity, and structural elements that could
impact MEP system performance.
2. Mechanical Systems Management
The mechanical systems that an MEP engineer manages include HVAC systems, fire
protection, elevators, and escalators. These systems are vital for maintaining comfortable
and safe indoor environments. MEP engineers design air conditioning systems that
regulate indoor temperature, humidity, and air quality. They also incorporate fire
protection elements like smoke extract ventilation and staircase pressurization
systems to ensure safe evacuation routes in emergencies.
In the UAE and other warm regions, MEP engineers focus on efficient heating and
ventilation solutions, prioritizing energy-efficient and environmentally friendly designs to
support sustainability goals.
3. Electrical System Planning and Design
In any building, the electrical system is essential for lighting, power distribution, and
communications. MEP engineers are responsible for creating a robust electrical
infrastructure that meets the building’s power demands while ensuring safety and
reliability. They handle mains and sub-mains distribution, internal and external lighting,
emergency lighting, and small power supplies throughout the building.
Additionally, MEP engineers integrate fire alarm and security systems within the
electrical layout to enhance safety measures. The electrical design must also include
lightning protection and earthing systems to prevent damage during storms, especially
in high-rise buildings.
4. Plumbing System Design and Coordination
Plumbing systems are critical for providing clean water and managing wastewater. MEP
engineers oversee incoming water mains services, cold and hot water supplies,
sanitary appliances, and drainage systems. They ensure that water flow and pressure
meet regulatory standards while optimizing water usage.
For commercial and industrial buildings, MEP engineers design complex water and
sewage treatment installations, supporting sustainable practices by managing water
resources efficiently. Rainwater systems are also incorporated to handle stormwater and
prevent flooding around the building site.
5. Energy Management and Sustainability
Energy management is an increasingly important area within MEP engineering, as
construction companies strive to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprints. MEP
engineers conduct energy modeling and thermal building simulations to assess a
building’s energy requirements. Using tools like daylight and artificial light simulations,
MEP engineers optimize lighting layouts to reduce electricity usage and improve occupant
comfort.
Environmental certification, such as BREEAM and LEED, is often a goal for modern
buildings, and MEP engineers ensure that designs meet these standards. They also
consider real weather data in simulations to improve energy efficiency, optimizing cooling
and heating systems for long-term sustainability.
6. Supervising MEP Installation and Construction
After designing the MEP systems, engineers oversee the installation to ensure that each
system is installed accurately according to the design plans. This supervision includes
coordinating with construction teams, managing cost control for materials, and
conducting quality checks.
Testing and commissioning are also vital steps, as MEP engineers evaluate each
system’s performance to ensure proper functionality. They perform acceptance tests and
make necessary adjustments before the final handover, ensuring that the building is safe,
comfortable, and operationally efficient.
7. Fire and Smoke Extraction, Escape Route Design
Safety is a priority in building design, and MEP engineers are responsible for creating
evacuation and escape routes. By conducting fire and smoke extraction simulations,
MEP engineers design paths for safe egress in emergencies. They configure optimal escape
routes to prevent congestion and allow occupants to exit safely.
Smoke extract ventilation is another critical area, as it allows for effective smoke removal
in case of fire. MEP engineers also incorporate staircase pressurization systems to
ensure that smoke does not block essential escape routes.
8. Cost Estimation and Budget Management
Throughout the MEP design and installation process, engineers play an active role in cost
estimation and budgeting. They prepare preliminary cost estimates, draft bills of
quantities, and oversee financial aspects related to MEP services, ensuring that the project
remains within budget. Accurate cost planning not only prevents overspending but also
allows for contingency measures in case unexpected costs arise.
9. System Optimization and Maintenance Planning
Beyond the initial installation, MEP engineers focus on system optimization and
maintenance planning. They use CFD flow simulation and building aerodynamics
to analyze system efficiency and make adjustments where needed. MEP engineers develop
maintenance plans that ensure equipment longevity and reduce future repair costs,
helping building owners manage long-term operational expenses.
Conclusion:
In summary, MEP engineers serve a multifaceted role within construction companies,
handling everything from design and installation of MEP systems to energy management
and maintenance planning. Their work ensures that buildings remain
functional, safe, and energy-efficient, contributing to a sustainable future in the
construction industry. By choosing qualified MEP professionals, companies can ensure
optimal system performance, regulatory compliance, and occupant comfort, making MEP
engineering an indispensable part of modern construction projects.